
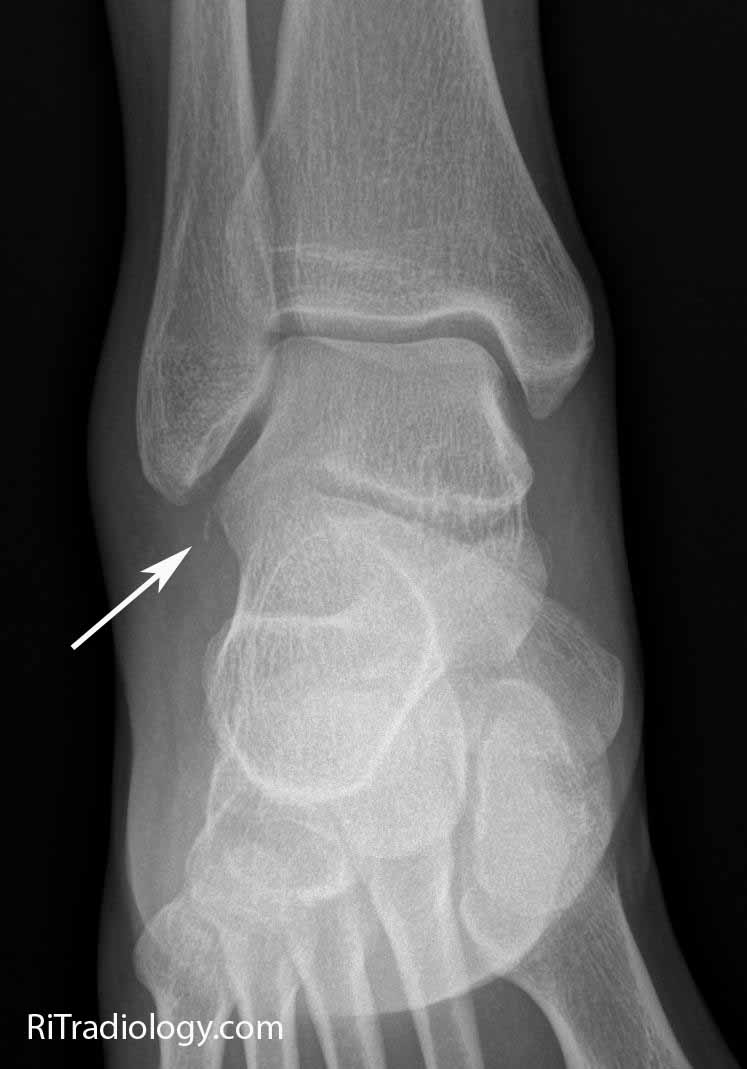

X-rays are the first line of investigation to assess ankle injury. Weight-bearing is determined by the patient's ability to take four steps. Patient unable to bear weight at the time of injury AND on arrival to the emergency department. Soft tissue integrity and the degree of swelling will affect the treatment choice and the timing of surgical fixation.Įxamination of the proximal fibula and the knee joint is required to avoid missing any higher injury as Maisonneuve fracture injury.Īnkle radiographs should be requested if there is pain or tenderness in either malleolus AND one of the following:
#Acute distal fibula fracture skin
Threatened skin of a deformed ankle necessitates urgent ankle reduction and splinting to reduce soft tissue stretching. If there is any clinical concern for vascular compromise or skin tenting, urgent ankle reduction should be attempted immediately in an attempt to regain vascular flow followed by neurovascular reassessment s Hand doppler is a quick and non-invasive method to assess the vascular flow in the foot. Neurological assessment should include the motor and sensory function of deep peroneal, superficial peroneal, tibial, sural medial, and lateral plantar nerves. Dorsalis pedis posterior tibial pulses should be assessed and compared to the contralateral side. Pale, cold foot indicates a critical vascular compromise. Neurovascular assessment includes the color and temperature of the foot. Ī documented neurovascular assessment is mandatory to be performed before and after any attempt for ankle manipulation. Therefore operative treatment is required to reduce and fix the fibula in the incisura fibularis. The poster tibial border blocks the fibula reduction. This is a rare type of ankle fracture dislocation where the fibula is posteriorly dislocated. Pilon fracture usually results from high energy axial loading trauma, e.g., fall from a high distance causing impaction of the talus against the tibial plafond. This injury is the comminuted fracture of the tibial plafond (distal end of the tibia, including the articular surface). This unstable injury requires operative treatment. Maisonneuve injury combines a proximal fibular fracture with tibiofibular syndesmosis and deltoid ligament injury with or without medial malleolus fracture. It is an unstable ankle injury caused by pronation external rotation injury. Injuries always occur in a cumulative pattern for example, a SER4 injury includes injuries of SER1, SER2, and SER3.
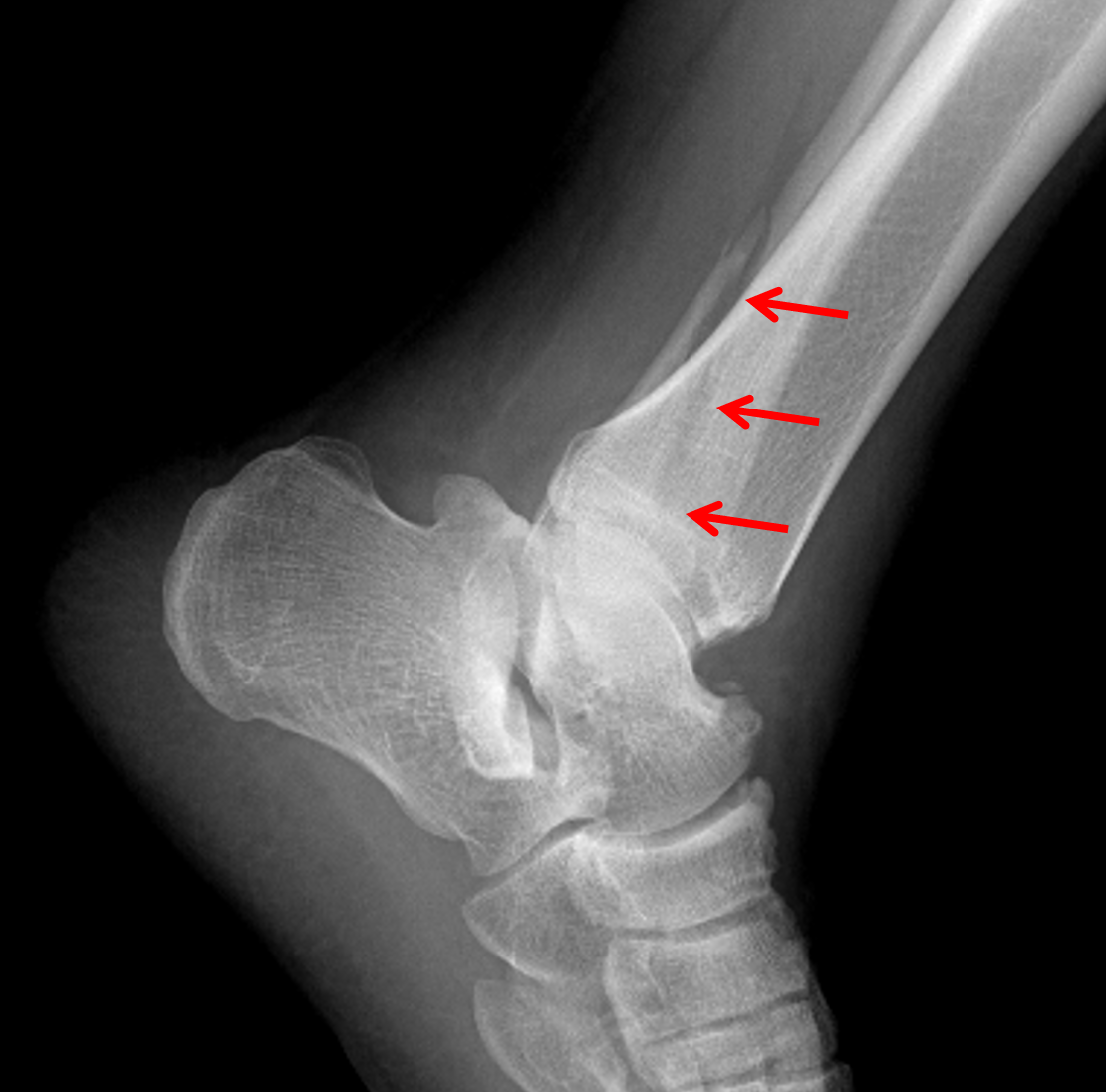
Ĭomminuted or transverse fibular fracture (proximal to tibial plafond) Branches from the peroneal, anterior, and posterior tibial arteries provide the arterial supply to the ankle joint. The ankle joint is innervated by articular branches from the tibial nerve, superficial and deep peroneal nerves. The lateral ligament complex resists the ankle from over the inversion. The lateral ligaments complex consists of three ligaments originating from the lateral malleolus and attaches to the talus (anterior and posterior talofibular ligaments) and the calcaneus(calcaneofibular ligament). The deltoid ligament originates from the medial malleolus and attaches to the talus, navicular, and calcaneus bones and stabilizes the ankle joint against over eversion. The syndesmosis is formed by three main parts the interosseous tibiofibular ligament, the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, and the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. The ankle syndesmosis is a fibrous joint connecting the distal tibia and fibula. The ankle joint entires three malleoli the lateral malleolus (distal end of the fibula), medial malleolus (medial lower end of the tibia), and the posterior malleolus.Īnkle joint stability is provided by the ankle mortise articulation with the talus body, the ankle syndesmosis, the ligaments and muscles around the ankle joint. The distal tibia and fibula articular portions together form the ankle mortice, which contains the body of talus bone. It is formed by the articulation between three bones distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus bone. The ankle joint is a hinge synovial joint that moves in one plane to produce dorsiflexion and plantar flexion. Treatment of these fractures aims to restore joint stability and alignment to reduce the risk of post-traumatic ankle arthritis. Ankle fractures are common injuries that could result from a trivial twisting injury in old frail patients up to high energy trauma in a young population.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
